Table Of Content
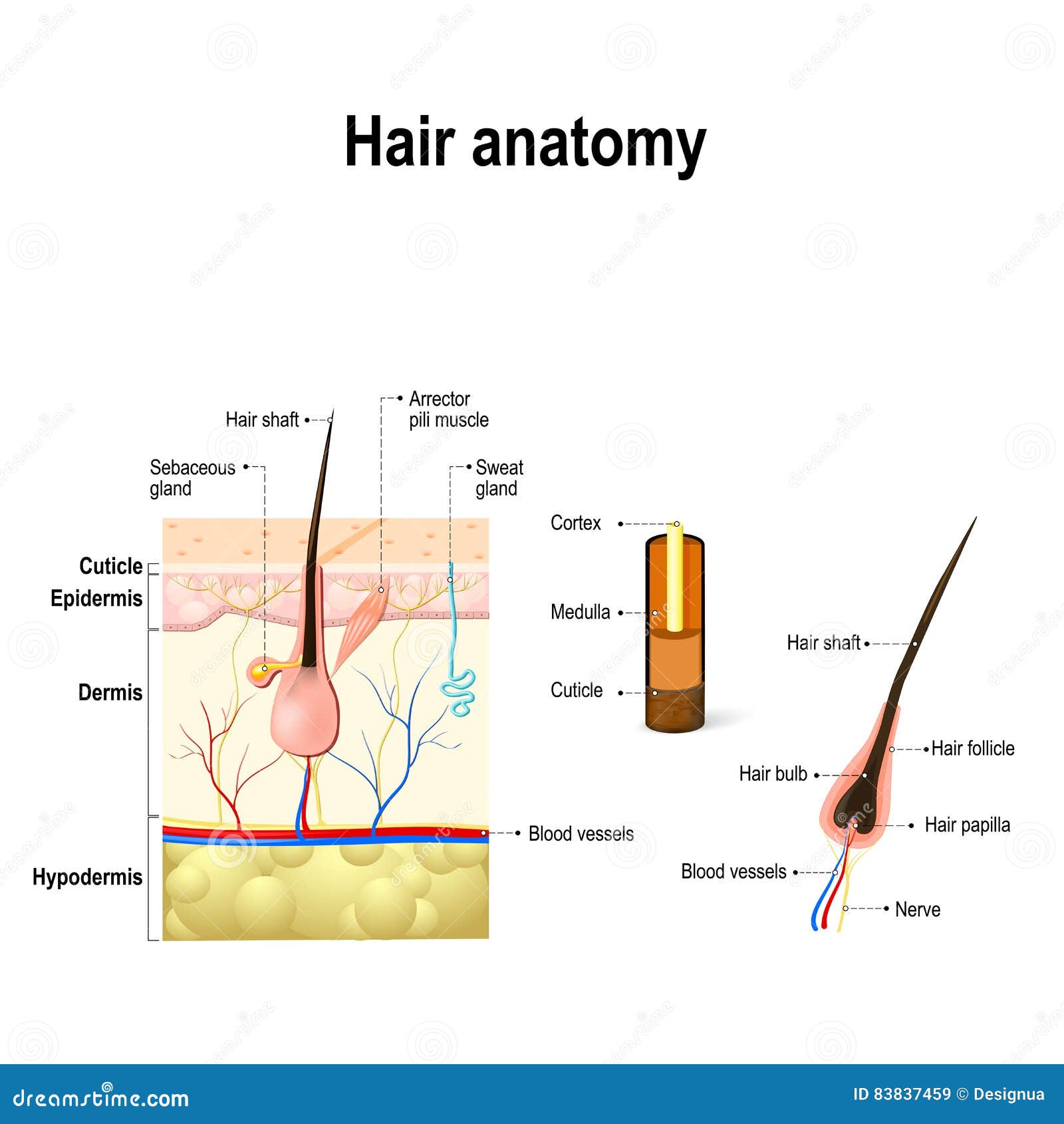
The color of the hair is determined by the amount of melanin in the hardened cells. This can vary a lot from person to person, and it changes over the course of a lifetime. The amount of melanin typically decreases as people get older, and more air gets trapped inside the hair – it then loses its color and turns white.
2. Structure of the hair
As you get older, your hair can change color, texture, and thickness. It can even change some of its location, with too much in some areas and too little in others. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. Telogen effluvium is usually temporary and doesn’t require treatment.
The Hair Growth Cycle
Furthermore, you can cut your hair or shave without damaging the hair structure because the cut is superficial. Most chemical hair removers also act superficially; however, electrolysis and yanking both attempt to destroy the hair bulb so hair cannot grow. We studied the molecular hair structure of several individuals using X-ray diffraction. Hair samples were collected from 12 healthy individuals of various characteristics, such as gender, optical appearance and genetic relation. Signals corresponding to the coiled-coil phase of the keratin molecules, the formation of intermediate filaments in the cortex and from the lipid molecules in the cell membrane complex were observed in the experiment.
Alopecia Areata
Your follicles can lose their ability to produce melanin as you age, which results in the growth of gray or white hair. Different follicles go through different phases of the cycle at the same time. Some follicles are in the growth phase while others might be in the resting phase.
Melatonin promotes the expression of MTNR1A (melatonin receptor 1A) in human and rex rabbit hair follicles (42, 43) and also enhances the expression of goat Wnt10b and beta-catenin (26). The signaling pathways involved in the regulation of hair follicle growth by melatonin are the PI3K/AKT signaling (43), Hippo, TGF-beta, MAPK signaling (13), and AKT/GSK3beta/beta-catenin signaling pathways (44). The results of the present study suggest that the MAPK signaling pathway is also at the forefront of KEGG enrichment. We have been focusing on the effects of the signaling pathways on reproduction (38). In addition, oral melatonin exerts a systemic effect on all cells, tissues, and organs, and it plays a key regulatory role in female reproduction (45). Therefore, the effect of embedded melatonin on goat litter size was considered in this study.
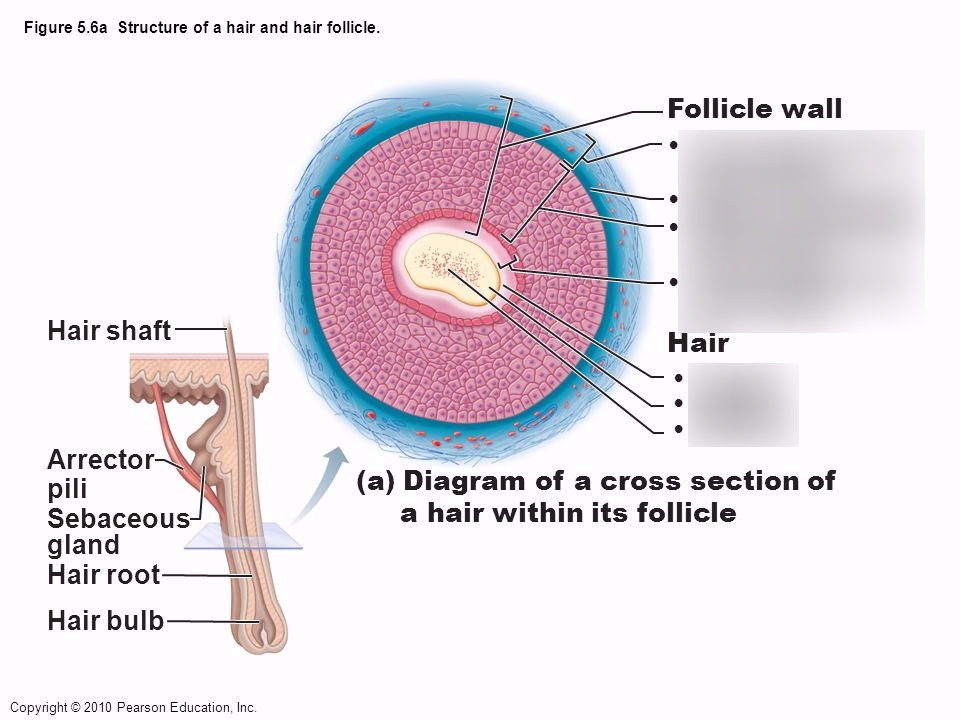
Hair bulb
Hair shaft synthesis and pigmentation only take place in anagen [11]. The degree of axial symmetry within the hair bulb determines the curvature of the final hair structure [35]. Fiber length is often dependent on the duration of the anagen or actively growing phase of the follicle [17]. The featured regulatory proteins in anagen phase are BMPs, sonic hedgehog, several WNT proteins and receptors. Insulin like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), fibroblast growth factor-7 hepatic growth factor (HGF), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) are thought to be important for anagen maintenance [36]. Lanugo, vellus and terminal hairs follow the same basic architectural principles.
Telogen Effluvium
New hair cells then start to multiply at the base of the “empty” hair follicle to form a new hair, and the growth phase of the hair growth cycle starts all over again. The shaft is the visible part of the hair that sticks out of the skin. The hair root is in the skin and extends down to the deeper layers of the skin. It is surrounded by the hair follicle (a sheath of skin and connective tissue), which is also connected to a sebaceous gland. The first to develop is the lanugo, a layer of downy, slender hairs that begin growing in the third or fourth month of fetal life and are entirely shed either before or shortly after birth.
Segmentally arranged basaloid follicular hamartomas (A) involving the... Download Scientific Diagram - ResearchGate
Segmentally arranged basaloid follicular hamartomas (A) involving the... Download Scientific Diagram.
Posted: Thu, 08 Feb 2018 08:12:08 GMT [source]
In the precortical matrix, these melanosomes are transferred to the hair shaft keratinocytes and formed a pigmented hair shaft. The hair follicle also contains melanocyte stem cells, which are located in the bulge and in the secondary hair [33–35]. In the second stage of development, hair germ elongates into a cord of epithelial cells and forms the hair peg (stages 3 and 4). It is surrounded by mesenchymal cells that eventually transformed to the fibrous sheath. Derived from the epithelial cells of the hair peg, hair matrix cells form the hair shaft and inner root sheath (IRS). Outer root sheath (ORS) generates two bulges along the side of the hair follicle, the proximal bulge serves as a reservoir for epithelial stem cells and the distal bulge evolves to sebaceous glands.
As matrix cells continue to proliferate, the hair follicle and hair will grow longer. This process defines the hair cycle, which further categorizes anagen, catagen, and telogen phases. Hair color is influenced by melanosome-producing melanocytes that rest within the layer of matrix cells. As the matrix cells of the germ layer continue to divide, they will eventually differentiate into the internal root sheath and keratin-producing cells (i.e., hair shaft cuticle and cortex layers discussed below). The infundibulum segment is the upper portion of the follicle. It begins at the surface of the epidermis and extends to the opening of the sebaceous duct.
In addition to appearance, the study also includes hair from a father and daughter, a pair of identical and a pair of fraternal twins to include genetic similarities. All hair was collected from healthy individuals and care was taken that the hair was not permed or dyed before the experiments. Alopecia areata [8] is an autoimmune disorder, meaning the body's immune system attacks its own hair follicles. Steroidal injections and topical creams slow down hair loss in this condition, but there is no cure to stop the hair fall completely.
Enhanced knowledge on the normal dynamics of the hair provides understanding the basis of how the follicle behaves during a disease. However recent progress in our understanding of the biology and pathology of hair follicles should lead more effective therapies for hair disorders. If hair is pulled out of the hair follicle, it can regrow.
These signals are related to the coiled-coils arrangement of the keratin proteins in the cortex, the formation of intermediate filaments in the cortex, and lipids in the cell membrane complex of the hair. Statistical analysis of the corresponding molecular dimensions revealed a rather small distribution between different individuals. These general properties of human hair are observed in all hair independent of gender, colour or optical appearance of the hair (as listed in Table 1) within the number of individuals included in this study.
In wool fibres as well as human hair, the cortical cells were observed to be divided into different regions termed orthocortex, paracortex and mesocortex (Mercer, 1953). The difference in distribution of these cell types is an important factor for determining the curvature of the hair fibre (Kajiura et al., 2006). In particular, straight hair tends to have symmetrical distribution of the ortho- and paracortices whereas curly hair tends to have a non-symmetrical distribution of these cortical cells (Kajiura et al., 2006). Most of the cortical cells are composed of a protein known as keratin (Robbins, 2012). The purpose of this study is to use X-ray diffraction to analyze the structure of human scalp hair for individuals with differing characteristics. The 12 individuals in this study include hair from men and women and hair of different colour and appearance, such as straight, wavy and curly.
In certain medical conditions, hair follicles can no longer grow hair and lead to bald spots or patches. The bulb is found at the root of your hair where the protein cells (keratin) grow to make hair. However, in curly hair, the way that the cells divide and produce certain proteins is asymmetrical and correlates with the bends in the curved follicle. This results in a hair fiber that has an elliptical shape, which allows it to curl. Vascular supply is provided by small arterioles originating in the subcutaneous fat. The vessels nourish the hair follicle by delivering oxygen and nutrients, eliminating waste, and promoting growth.
No comments:
Post a Comment